
At medlife , we’re on a mission to transform health outcomes by spreading knowledge, fostering conversation, and empowering communities to take control of their well-being. From engaging workshops to high-energy events, our Health Awareness Program brings vital health education directly to YOU. Get involved, get informed, and let’s make health a priority for everyone!
Infrastructure Enhancement involves upgrading healthcare facilities to improve the overall patient experience. This includes modernizing buildings, ensuring accessibility, and creating a comfortable environment for patients.
Investing in health infrastructure enhances patient outcomes and strengthens the overall healthcare system. By focusing on facility upgrades, equipment provision, mobile health units, safe water access, supply chain support, and waste disposal systems, we can create a more effective and sustainable healthcare environment for everyone.


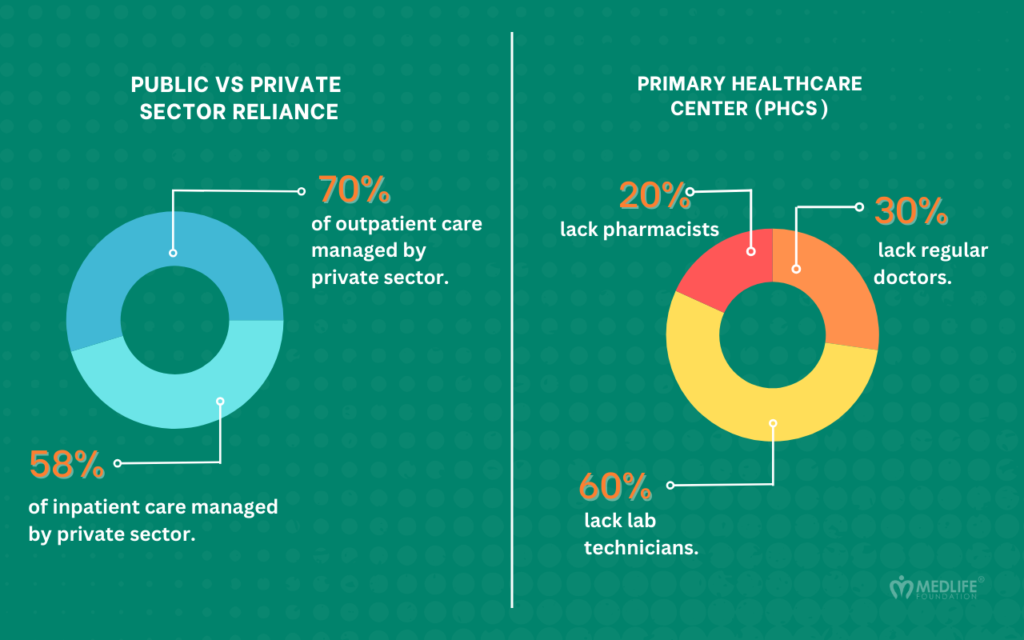
We’re dedicated to elevating healthcare experiences by tackling fundamental infrastructure needs, supplying essential resources, and delivering critical care services directly to communities.
Infrastructure Enhancement
“Transforming Facilities, Transforming Lives”
Upgrading healthcare facilities to ensure patients experience comfort, safety, and quality care in every visit.
Equipment Provision
“Equipping for Excellence”
Providing essential medical tools and devices that empower healthcare providers to deliver precise, quality treatment.
Mobile Health Units
“Bringing Health to Your Doorstep”
Deploying mobile clinics that reach remote and underserved areas, making quality care accessible to everyone.
Safe Water Access & Hygiene Stations
“Pure Water, Better Health”
Establishing clean water and hygiene stations to promote health, prevent infections, and support safe healthcare practices.
Supply Chain Support
“Consistent Care Through Continuous Supply”
Ensuring reliable access to essential medications, so communities never face shortages in critical times.
Waste Disposal Systems
“Safety and Sustainability in Every Step”
Implementing eco-friendly, safe waste disposal systems to keep healthcare spaces clean, compliant, and environmentally responsible.

Medlife Foundation is dedicated to improving healthcare access for underserved communities, providing essential medical services, health education, and support to create healthier lives.